How do Organisms Reproduce – Textbook Exercise Questions
1. Asexual reproduction takes place through budding in:
(b) Yeast
In budding, a small bud-like outgrowth forms on the parent cell, which then detaches to become a new individual. This is a common method of reproduction in yeast.
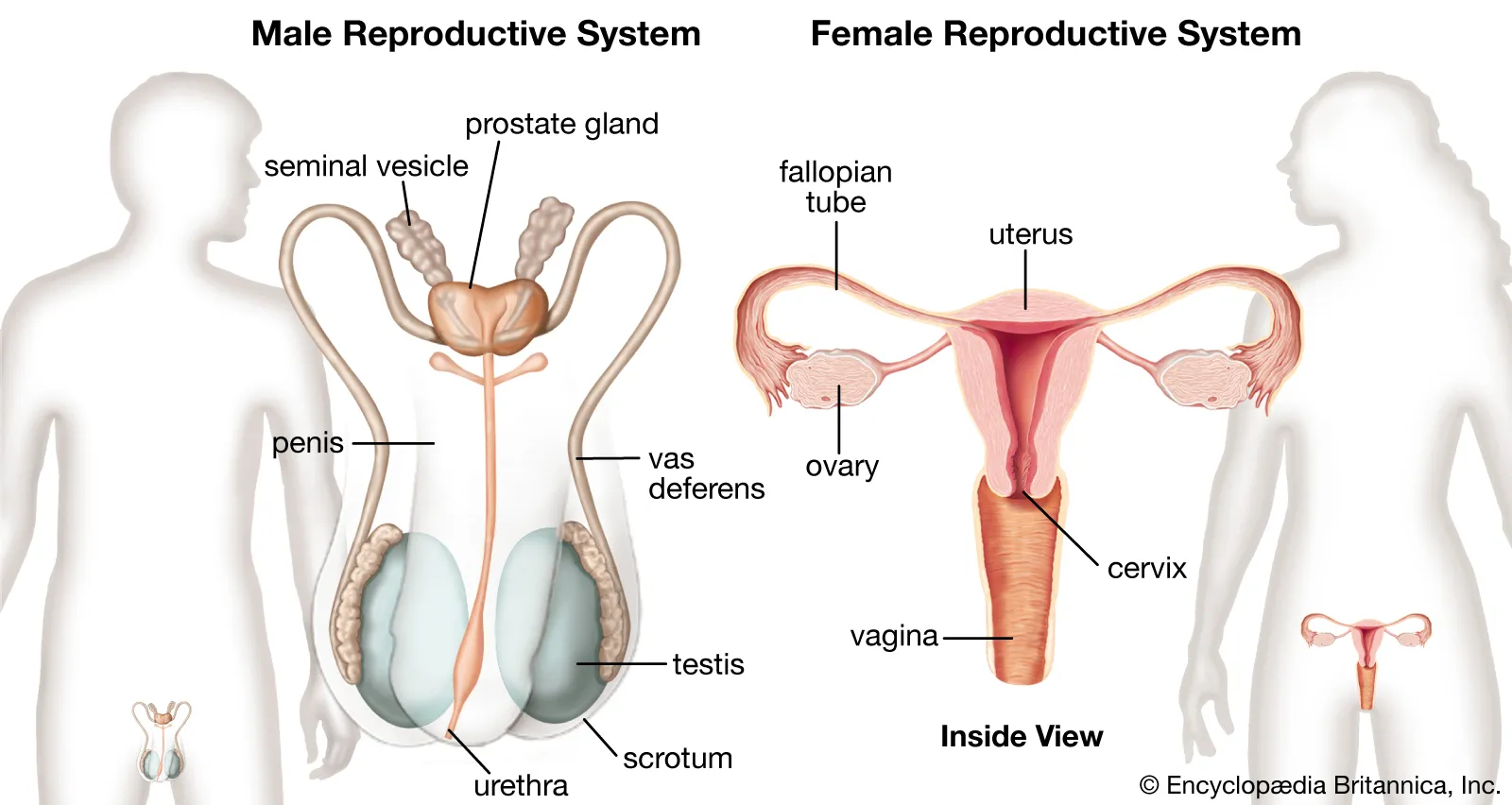
2. Which of the following is not a part of the female reproductive system in human beings?
(c) Vas deferens
The vas deferens is a part of the male reproductive system that carries sperm from the testis. The ovary, uterus, and fallopian tube are all parts of the female reproductive system.
3. The anther contains:
(d) Pollen Grains
The anther is the part of the stamen (the male reproductive part of a flower) where pollen grains are produced.
4. What are the advantages of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction?
Sexual reproduction involves two parents and the fusion of their gametes. This mixing of DNA creates genetic variation in the offspring. This variation is a major advantage because it helps the species to adapt to changes in the environment, increasing the chances of survival if conditions change. Asexual reproduction produces genetically identical offspring, which are all vulnerable to the same diseases and environmental changes.
5. What are the functions performed by the testis in human beings?
The testes have two main functions:
-
Production of sperm: They produce the male gametes, called sperm.
-
Production of hormones: They secrete the male sex hormone, testosterone, which is responsible for the development of male secondary sexual characteristics (like a deeper voice and facial hair).
6. Why does menstruation occur?
Every month, the uterus prepares itself to receive a fertilized egg by building up a thick lining of blood and tissue. If the egg released by the ovary is not fertilized, this lining is no longer needed. The body then breaks down this lining, which is discharged through the vagina as blood and mucus. This monthly cycle is called menstruation.
7. Draw a labelled diagram of the vertical section of a flower.
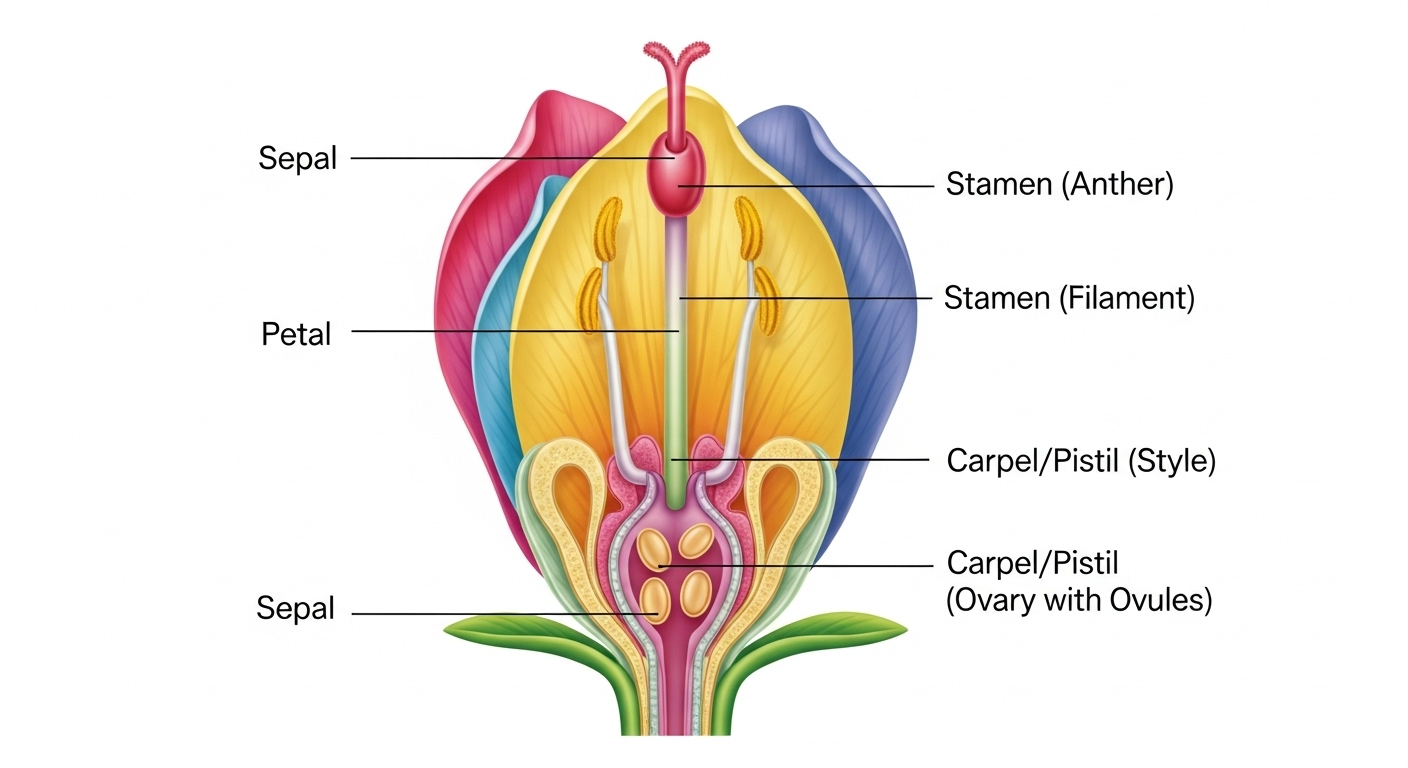
8. What are the different methods of contraception?
Contraception methods are used to prevent pregnancy. The main types are:
-
Barrier Methods: These physically prevent sperm from reaching the egg. Examples include condoms and diaphragms.
-
Chemical Methods: These use hormones to prevent the release of eggs or thicken cervical mucus. Examples include oral contraceptive pills and vaginal rings.
-
Intra-Uterine Devices (IUDs): Devices like the Copper-T are placed in the uterus to prevent the implantation of a fertilized egg.
-
Surgical Methods: These are permanent methods. Vasectomy in males (blocking the vas deferens) and Tubectomy in females (blocking the fallopian tubes) prevent the transport of gametes.
9. How are the modes of reproduction different in unicellular and multicellular organisms?
Unicellular organisms, being very simple, reproduce by simple asexual methods like binary fission or budding, where the parent cell divides to form new individuals. Multicellular organisms have complex bodies with specialized cells and tissues. Therefore, they often use more complex methods of reproduction. While some can reproduce asexually (like plants through vegetative propagation), many use sexual reproduction, which involves specialized reproductive organs and the formation of gametes.
10. How does reproduction help in providing stability to populations of species?
Reproduction ensures the continuity of a species by producing new individuals to replace the ones that die. It helps maintain a stable population. Furthermore, sexual reproduction introduces genetic variations. This variation is crucial for the population’s stability because it allows the species to adapt to environmental changes, resist diseases, and evolve over time, preventing it from becoming extinct.
11. What could be the reasons for adopting contraceptive methods?
People adopt contraceptive methods for several reasons:
-
To prevent unwanted pregnancies: This allows for family planning and choosing when to have children.
-
To maintain a gap between children: This is important for the health of the mother and for providing adequate care to each child.
-
To control population growth: Limiting family size helps manage national and global population levels.
-
To prevent the transmission of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs): Barrier methods like condoms are effective in preventing the spread of STDs.
InText Questions
1. What is the importance of DNA copying in reproduction?
DNA copying (or replication) is crucial because DNA contains the genetic blueprint for all the characteristics of an organism. During reproduction, a copy of this DNA is passed from the parent to the offspring. This ensures that the offspring inherits the necessary genetic information to develop and function like its parent, thus maintaining the species’ characteristics.
2. Why is variation beneficial to the species but not necessarily for the individual?
Variation means there are differences among individuals in a species. This is beneficial for the species because if the environment changes (e.g., a new disease appears or the temperature rises), some individuals with specific variations might be able to survive and reproduce, ensuring the continuation of the species. However, for an individual, a particular variation might not be advantageous and could even be harmful in the current environment, potentially reducing its chances of survival.
3. How does binary fission differ from multiple fission?
While both are methods of asexual reproduction in unicellular organisms, binary fission and multiple fission are different in their process, the number of offspring they produce, and the conditions under which they typically occur.
| Basis of Difference | Binary Fission | Multiple Fission |
| Meaning | The parent cell divides into two new daughter cells. “Bi” means two. | The parent cell divides into many new daughter cells simultaneously. “Multi” means many. |
| Process of Division | First, the nucleus divides into two, followed by the division of the cytoplasm, splitting the cell into two. | The nucleus divides repeatedly to form many smaller nuclei. Cytoplasm then gathers around each nucleus. |
| Protective Covering | No protective wall (cyst) is formed around the parent cell during the process. | The parent cell often develops a thick, protective wall around itself called a cyst. |
| Conditions | This usually happens during favorable conditions, when there is plenty of food and the temperature is suitable. | This is often a response to unfavorable conditions. The cyst protects the cell until conditions improve. |
| Outcome | Two independent daughter cells are formed from one parent. | The cyst breaks open when conditions become favorable, releasing all the daughter cells at once. |
| Example | Amoeba, Paramecium | Plasmodium (the malarial parasite) |
4. How will an organism be benefited if it reproduces by spores?
Spores have thick protective walls that allow them to survive in unfavorable conditions like extreme heat, cold, or dryness. They are also very light and can be easily dispersed by wind, water, or animals over large distances. This helps the organism to spread widely and survive harsh periods.
5. Can you think of reasons why more complex organisms cannot give rise to new individuals through regeneration?
More complex organisms, like humans, are made of highly specialized tissues and organs. Their cells differentiate to perform specific functions and cannot easily change back to create all the different cell types needed for a new individual. Regeneration of a whole organism requires a simple body plan where cells are less specialized.
6. Why is vegetative propagation practised for growing some types of plants?
Vegetative propagation is practised for several reasons:
-
It is a faster way to grow plants compared to growing them from seeds.
-
Plants grown this way will be genetically identical to the parent, so desirable traits (like fruit quality or flower color) are guaranteed.
-
It can be used to grow plants, like bananas and some varieties of grapes, that produce few or no viable seeds.
7. Why is DNA copying an essential part of the process of reproduction?
DNA copying is essential because it is the process that creates a new copy of the organism’s genetic material to be passed on to the next generation. Without an accurate copy of DNA, the offspring would not receive the complete set of instructions needed for its development and survival, and the characteristics of the species would be lost.
8. How is the process of pollination different from fertilisation?
Pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from the anther (male part) to the stigma (female part) of a flower. Fertilisation is the fusion of the male gamete (from the pollen grain) with the female gamete (the egg, inside the ovule). Pollination must happen before fertilisation can occur.
9. What is the role of the seminal vesicles and the prostate gland?
The seminal vesicles and the prostate gland are accessory glands in the male reproductive system. They produce a fluid called seminal plasma. This fluid mixes with the sperm to form semen. The fluid nourishes the sperm and makes their transport easier.
10. What are the changes seen in girls at the time of puberty?
Puberty is the time when the body becomes sexually mature. The changes seen in girls include:
-
Growth of breasts.
-
Widening of the hips.
-
Growth of hair in the pubic region and under the arms.
-
The start of the menstrual cycle (menstruation).
11. How does the embryo get nourishment inside the mother’s body?
The embryo gets nourishment through a special tissue called the placenta. The placenta is a disc-like structure embedded in the uterine wall that connects the mother to the developing embryo. Through the placenta, nutrients and oxygen pass from the mother’s blood to the embryo’s blood, and waste products from the embryo pass to the mother’s blood to be eliminated.
12. If a woman is using a copper-T, will it help her in protecting from sexually transmitted diseases?
No. A copper-T is an intra-uterine device (IUD) that prevents pregnancy by stopping a fertilized egg from implanting in the uterus. It does not provide a barrier against the exchange of bodily fluids. Therefore, it offers no protection against sexually transmitted diseases (STDs).
Male and Female Reproduction Organs