Control and Coordination – Textbook Exercise Questions
1. Which of the following is a plant hormone?
(D) Cytokinin.
Insulin, thyroxin, and oestrogen are all hormones found in animals. Cytokinin is a plant hormone that promotes cell division.
2. The gap between two neurons is called a:
(B) Synapse.
A synapse is the small gap at the end of a neuron that allows a signal to pass from one neuron to the next.
3. The brain is responsible for:
(D) All of the above.
The brain is the main control center of the body. It is responsible for complex functions like thinking, involuntary actions like regulating the heartbeat, and maintaining balance.
4. What is the function of receptors in the body? Think of situations where receptors do not work properly. What problems are likely to arise?
The function of receptors is to detect stimuli from the environment. These are specialized cells that sense changes like heat, light, sound, smell, and touch and convert them into electrical signals for the nervous system.
If receptors do not work properly, the body cannot sense changes in its surroundings. For example, if the pain receptors in our skin are damaged, we might get severely burned without realizing we are touching something hot. If taste or smell receptors fail, we might not be able to detect spoiled food, which could lead to food poisoning.
5. Draw a labelled diagram of a neuron and explain its function.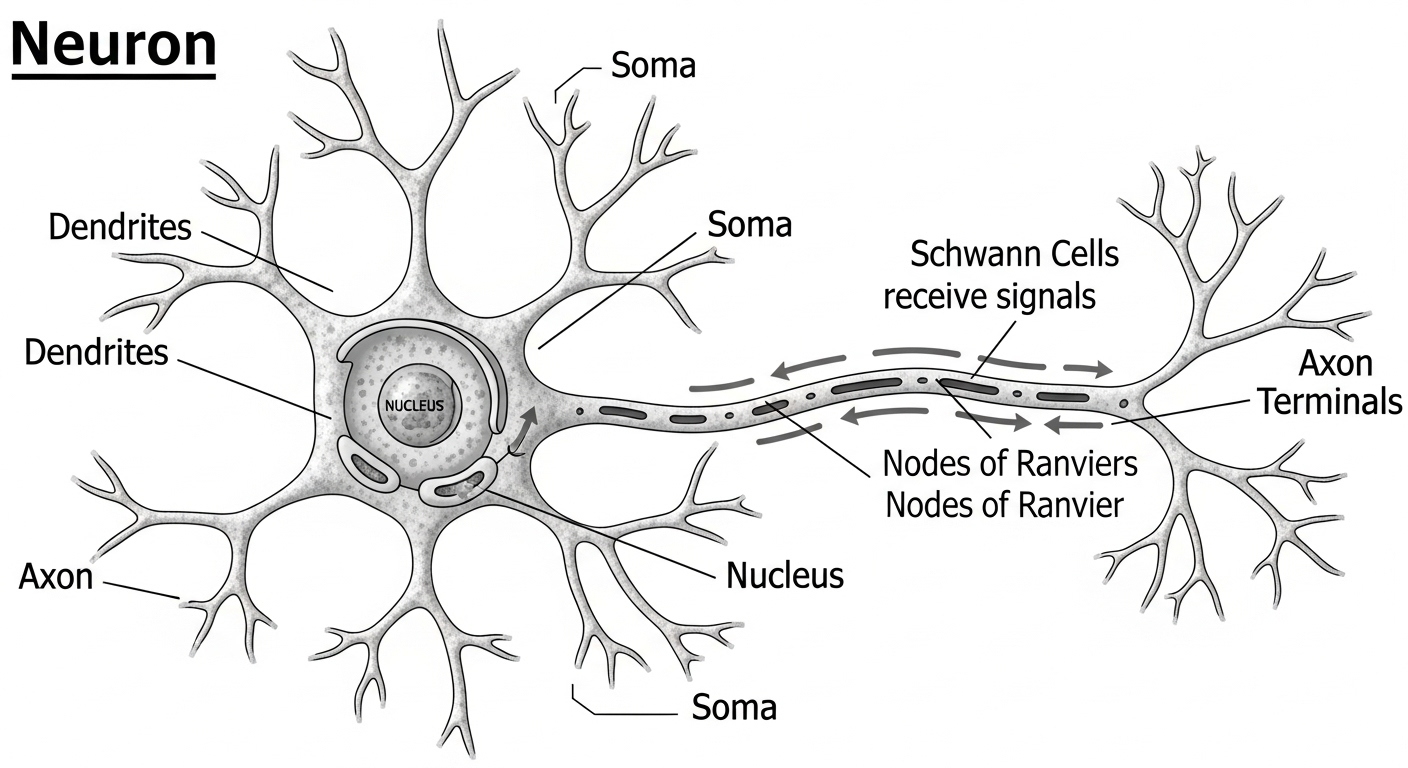
Function: The function of a neuron, or nerve cell, is to transmit information in the form of electrical and chemical signals. Dendrites receive signals from other neurons. The cell body processes these signals. The axon carries the signal over a long distance, and the axon terminal passes the signal on to the next neuron across a synapse.
6. How does phototropism occur in plants?
Phototropism is the growth of a plant in response to a light stimulus. This happens because of a plant hormone called auxin.
-
Auxin is produced at the tip of the shoot.
-
When light comes from one direction, auxin moves to the shaded side of the shoot.
-
The high concentration of auxin on the shaded side makes the cells there grow longer and faster than the cells on the lighted side.
-
This unequal growth causes the shoot to bend and grow towards the light source.
7. Which signals will get disrupted in case of a spinal cord injury?
In case of a spinal cord injury, the signals traveling between the brain and the parts of the body below the injury get disrupted. This includes:
-
Motor signals from the brain to the body, which control movement. This can lead to paralysis.
-
Sensory signals from the body to the brain, which carry sensations like touch, pain, and temperature. This can lead to a loss of feeling.
8. How does chemical coordination occur in plants?
Chemical coordination in plants is carried out by plant hormones, also known as phytohormones. These chemicals are produced in one part of the plant and are transported to other parts to control processes like growth, development, and response to the environment. For example, auxin promotes shoot growth, cytokinins promote cell division, and abscisic acid inhibits growth.
9. What is the need for a system of control and coordination in an organism?
A system of control and coordination is essential for an organism to survive and function properly. It is needed to:
-
Respond and adapt to changes in the environment (e.g., pulling your hand away from a hot object).
-
Ensure that different parts of the body work together in an organized way (e.g., muscles, bones, and nerves working together to allow movement).
-
Maintain a constant internal environment (homeostasis), like regulating body temperature and blood sugar levels.
10. How are involuntary actions different from reflex actions?
| Basis of Difference | Involuntary Action | Reflex Action |
| Definition | An action that occurs without the conscious choice of an organism. | A rapid and automatic response to a specific stimulus. |
| Control Center | It is controlled by the mid-brain and hind-brain (e.g., medulla). | It is primarily controlled by the spinal cord. |
| Speed | The response is generally slow and steady. | The response is extremely fast and immediate. |
| Example | The beating of the heart, breathing, and digestion. | Pulling your hand away from a hot object, sneezing, or blinking when something nears your eye. |
11. Compare and contrast the nervous and hormonal mechanisms for control and coordination in animals.
| Basis of Difference | Nervous System | Hormonal (Endocrine) System |
| Signal | Information is sent as electrical impulses. | Information is sent as chemical messengers called hormones. |
| Transmission Pathway | Signals travel along nerve fibers (neurons). | Hormones travel through the bloodstream. |
| Speed of Transmission | Extremely fast, with almost instant responses. | Relatively slow, taking seconds, minutes, or even hours. |
| Duration of Effect | The effect is usually short-lived. | The effect is generally longer-lasting. |
| Target Area | The response is localized and specific to certain muscles or glands. | The response can be widespread, affecting multiple organs at once. |
12. What is the difference between the manner in which movement takes place in a sensitive plant and the movement in our leg?
| Basis of Difference | Movement in a Sensitive Plant (e.g., Mimosa) | Movement in Our Leg |
| Nature of Response | It is a non-directional response to a stimulus (like touch). It is not related to growth. | It is a voluntary, directional, and highly controlled action. |
| Underlying Mechanism | The movement is caused by a rapid change in water pressure (turgor pressure) within the cells at the base of the leaves. | The movement is caused by the coordinated contraction and relaxation of specialized muscle tissues. |
| Tissues Involved | No specialized muscle or nervous tissues are involved. | It involves a complex interplay of the skeletal system, muscular system, and nervous system. |
| Control System | The response is triggered by chemical signals that spread through the plant cells. | The action is controlled by electrical impulses from the brain and spinal cord sent through nerves. |
InText Questions
1. What is the difference between a reflex action and walking?
A reflex action is an involuntary and rapid response to a stimulus, controlled by the spinal cord without conscious thought (e.g., sneezing). Walking is a voluntary action that we consciously decide to do. It is a complex activity controlled by the brain that involves coordinated muscle movements.
2. What happens at the synapse between two neurons?
At a synapse, an electrical signal from the first neuron’s axon triggers the release of chemical messengers called neurotransmitters into the gap. These chemicals travel across the synapse and bind to receptors on the dendrites of the next neuron, starting a new electrical signal in it.
3. Which part of the brain maintains posture and equilibrium of the body?
The cerebellum, located in the hind-brain, is responsible for maintaining the posture, balance, and equilibrium of the body.
4. How do we detect the smell of an agarbatti (incense stick)?
When an agarbatti burns, tiny chemical particles are released into the air. These particles enter our nose and are detected by olfactory receptors located in the nasal cavity. These receptors send an electrical signal to the forebrain, which interprets the signal as a specific smell.
5. What is the role of the brain in a reflex action?
While the reflex action itself is controlled by the spinal cord for a quick response, the information also travels to the brain. The brain’s role is to make us aware of the event after it has happened. For example, the spinal cord makes you pull your hand away from a hot object instantly, and a moment later, your brain registers the pain and makes you aware of what happened.
6. What are plant hormones? Name any two.
Plant hormones (or phytohormones) are chemical compounds produced by plants that regulate their growth, development, and responses to the environment.
Two plant hormones are Auxin and Gibberellin.
7. How is the movement of leaves of the sensitive plant different from the movement of a shoot towards light?
The movement of the leaves of a sensitive plant (e.g., touch-me-not) is a rapid response to touch that does not involve growth. It is caused by changes in water pressure in the cells. In contrast, the movement of a shoot towards light (phototropism) is a slow, directional growth response caused by the unequal distribution of the growth hormone auxin.
8. Give an example of a plant hormone that promotes growth.
Auxin is a plant hormone that promotes cell elongation and is responsible for the growth of shoots and roots.
9. How do auxins promote the growth of a tendril around a support?
When a tendril touches a support, the auxin hormone moves to the side of the tendril that is away from the support. This causes the cells on the side not touching the support to grow faster than the cells on the side that is in contact. This unequal growth makes the tendril bend and coil around the support.
10. Design an experiment to demonstrate hydrotropism.
-
Take a transparent box and fill it with moist soil.
-
Plant a germinating seed near one wall of the box.
-
Place a small clay pot with holes at the bottom in the soil on the opposite side of the seed and fill it with water.
-
After a few days, you will observe that the root of the seedling grows towards the clay pot.
This demonstrates hydrotropism, as the root grows towards the source of water, bending away from its normal downward path.
11. How does chemical coordination take place in animals?
Chemical coordination in animals is carried out by the endocrine system. This system is made up of endocrine glands that produce and secrete chemical messengers called hormones directly into the bloodstream. These hormones travel throughout the body and act on specific target cells or organs to regulate processes like growth, metabolism, and stress responses.
12. Why is the use of iodised salt advisable?
Iodine is essential for the thyroid gland to produce the hormone thyroxine. Thyroxine regulates the body’s metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. A lack of iodine in the diet can cause the thyroid gland to swell, a condition called goitre. Using iodised salt ensures that the body gets enough iodine to produce thyroxine and function properly.
13. How does our body respond when adrenaline is secreted into the blood?
When adrenaline is secreted, it prepares the body for a “fight or flight” response to an emergency situation. The effects include:
-
The heart beats faster to supply more oxygen to the muscles.
-
Breathing rate increases.
-
Blood pressure rises.
-
Blood flow is diverted from the digestive system to the skeletal muscles.
-
The liver releases more glucose into the blood for a quick energy boost.
14. Why are some patients with diabetes treated by giving injections of insulin?
Diabetes is a condition where the body cannot regulate blood sugar levels. In Type 1 diabetes, the pancreas does not produce enough of the hormone insulin. Insulin is needed to help cells absorb glucose from the blood for energy. Patients are given injections of insulin to make up for this deficiency, which helps lower their blood sugar levels and allows their bodies to use glucose properly.